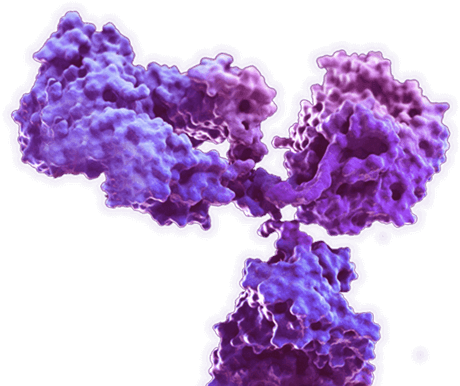
Cell markers is known as cell surface antigens, which can be used to help identify and classify cells.
Signal Pathway is the process by which a chemical or physical signal is transmitted through a cell as a series of molecular events, most commonly protein phosphorylation catalyzed by protein kinases, which ultimately results in a cellular response.
Cell biology is a branch of biology studying the structure and function of the cell, also known as the basic unit of life. Cell biology encompasses both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells and can be divided into many sub-topics which may include the study of cell metabolism, cell communication, cell cycle, and cell composition.
Epigenetics is the study of heritable phenotype changes that do not involve alterations in the DNA sequence. Epigenetics most often involves changes that affect gene activity and expression, but the term can also be used to describe any heritable phenotypic change.
Metabolism is the set of life-sustaining chemical reactions in organisms. A striking feature of metabolism is the similarity of the basic metabolic pathways among vastly different species.

Immunology is a branch of biology that covers the study of immune systems in all organisms. Immunology has applications in numerous disciplines of medicine, particularly in the fields of organ transplantation, oncology, rheumatology, virology, bacteriology, parasitology, psychiatry, and dermatology.

Microbiology is the study of microorganisms, those being unicellular (single cell), multicellular (cell colony), or acellular (lacking cells). Microbiology encompasses numerous sub-disciplines including virology, bacteriology, protistology, mycology, immunology and parasitology.

Neuroscience (or neurobiology) is the scientific study of the nervous system. It is a multidisciplinary branch of biology that combines physiology, anatomy, molecular biology, developmental biology, cytology, mathematical modeling, and psychology to understand the fundamental and emergent properties of neurons and neural circuits.
Stem cells are undifferentiated or partially differentiated cells that can differentiate into various types of cells and divide indefinitely to produce more of the same stem cell.

Apoptosis is a form of programmed cell death that occurs in multicellular organisms. Viability measurements may be used to evaluate the death or life of cancerous cells and the rejection of implanted organs.
Glycobiology is the study of the structure, biosynthesis, and biology of saccharides (sugar chains or glycans) that are widely distributed in nature. Sugars or saccharides are essential components of all living things and aspects of the various roles they play in biology are researched in various medical, biochemical and biotechnological fields.

Autophagy is the natural, regulated mechanism of the cell that removes unnecessary or disfunctional components. Autophagy is essential for basal homeostasis; it is also extremely important in maintaining muscle homeostasis during physical exercise.

Cancer Research is a peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the American Association for Cancer Research. It covers research on all aspects of cancer and cancer-related biomedical sciences and was established in 1941.

Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is a class of diseases that involve the heart or blood vessels. CVD includes coronary artery diseases (CAD) such as angina and myocardial infarction (commonly known as a heart attack).

Infectious diseases are caused by pathogenic microorganisms, such as bacteria, viruses, parasites or fungi; the diseases can be spread, directly or indirectly, from one person to another.

A genetic disorder is a disease caused in whole or in part by a change in the DNA sequence away from the normal sequence. The disease is passed from one generation to the next, but does not necessarily appear in each generation.

Rare disease is defined as one that affects fewer than 200,000 people. The prevalence of a rare disease usually is an estimate and may change over time.

Chemical compound, any substance composed of identical molecules consisting of atoms of two or more chemical elements.

Animal research is the process of using non-human animals to control variables that may affect biological systems or behaviors in experiments.

Plant Biology is a peer-reviewed scientific journal of plant biology. Plant Biology is an international journal of broad scope bringing together different subdisciplines, such as physiology, molecular biology, cell biology, development, genetics, systematics, ecology, evolution, ecophysiology, plant-microbe interactions, and mycology.