Overview
Arabidopsis, a small plant in the brassica family, has become the model system of choice for plant biology research. Significant progress has been made in plant growth and development research by focusing on the molecular genetics of this simple angiosperm. Relying on the high-throughput molecular design platform and plant genetic transformation system, Creative Biolabs is committed to the development and application of gene editing technology, and provide "one-stop" technical services for the research of functional genes.
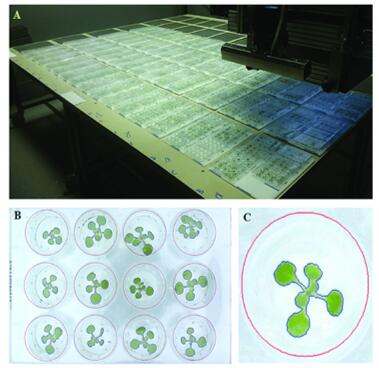
Fig 1. High-throughput phenotyping platform for growing Arabidopsis in multi-well plates. (De Diego N, 2017)
The Novel Breeding of Favorable Genes
Some genes related to seed dormancy and germination have been verified from Arabidopsis mutants, which will help to understand the mechanism of seed germination and dormancy.
Gibberellic acid (GA) is one of the key factors to promote seed germination. Genes such as RGL, SPY, GCR, SLY, and GAR are involved in GA-promoting seed germination, while ABI1, ABI2, ABI3, ABI4, ABI5, FUS3, LEC, MARD and CIPK are related to the induction of abscisic acid (ABA) in seed dormancy. Phytochromes PhyA, PhyB, PhyC, PhyD, and PhyE are photoreceptors that regulate the expression of other germination-related genes through phosphorylation.
The Arabidopsis Information Resource (TAIR) maintains a database of genetic and molecular biology data for the model plant Arabidopsis. Data provided by TAIR include the complete genome sequence as well as gene structure, gene product information, gene expression, DNA and seed banks, genome maps, genetic and physical markers, publications, and information about the Arabidopsis research community.
Technical Application
- Arabidopsis has a small genome, a short life cycle, and is prone to mutagenesis. Arabidopsis research is relevant to neurological diseases, such as cellular processes associated with neurodegenerative diseases, such as Alzheimer's disease and Parkinson's disease, and the neurological disease Friedreich Ataxia.
- CRISPR-Cas9-Mediated Chromosome Engineering in Arabidopsis.
Mb-wide chromosomal rearrangements, such as inversions and translocations, were obtained in Arabidopsis by combining highly efficient staphylococcus aureus Cas9 (SaCas9) with an egg cell-specific promoter to facilitate heritable mutations.
- Overexpression of MxbHLH18 increases tolerance to iron and high-salt stress in Arabidopsis.
- ROS as key players in quinolone antibiotic stress in Arabidopsis: from the perspective of photosystem function, oxidative stress and phyllosphere microbiome.
- Using single-cell transcriptomic analysis to map developmental trajectories and assess cell-type-specific changes during heat shock demonstrates that single-cell transcriptomics holds promise for studying plant development and plant physiology at unprecedented resolution.
Technical Platform
Creative Biolabs offers the modelorg technical platform for different species, including custom service to suit your needs. Please feel free to contact us.
Reference
- De, Diego.N.; et al. An automated method for high-throughput screening of Arabidopsis rosette growth in multi-well plates and its validation in stress conditions. Frontiers in plant science, 2017, 8: 1702.